Fermi Telescope
NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope is a powerful space observatory that detects gamma rays, the most energetic form of light. Fermi enables scientists to address questions across a broad range of topics, from crushed stellar remnants like pulsars and the origin of high-energy charged particles called cosmic rays to stellar explosions known as gamma-ray bursts.
Fermi observes light with energies thousands to hundreds of billions of times greater than what our eyes can detect. The energy of the light we can see ranges from about 2 to 3 electron volts. Fermi observes light in the energy range between 8,000 electron volts (8 keV) to greater than 300 billion electron volts (300 GeV). As a result, the gamma-ray sky looks spectacularly different than the one we see at night, as shown in the image at the top of the page constructed from 12 years of Fermi observations greater than 1 GeV.
The satellite launched on June 11, 2008, as the Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope. Shortly thereafter, NASA renamed the observatory in honor of Professor Enrico Fermi (1901-1954), a pioneer in high-energy physics.
Since then, Fermi has discovered more than some 300 gamma-ray pulsars, including the first one found beyond our own galaxy. Fermi has shown that giant flares from supermagnetized neutron stars can be detected in galaxies beyond our own. Its measurements have provided important limits on new theories of gravity and of the nature of dark matter, the mysterious substance that seems to bind galaxies together. Fermi data revealed a vast new component of our galaxy known as the Fermi Bubbles, a structure that spans 50,000 light-years and likely formed as a result of an outburst from the monster black hole at the center of our galaxy.
What Are Gamma Rays?
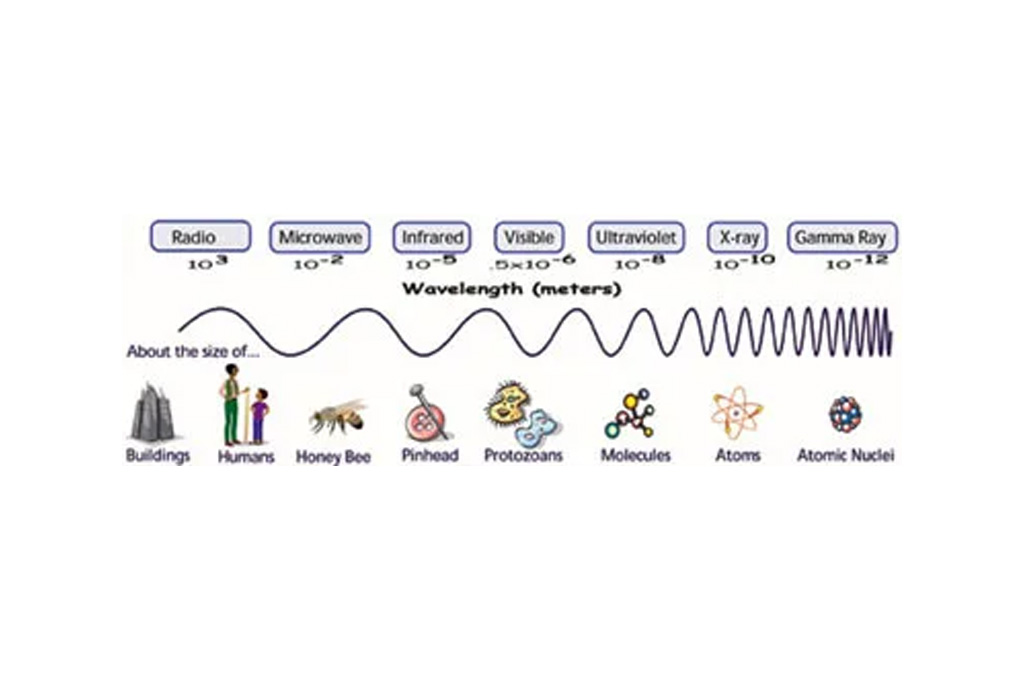
Light energy comes in many different forms. People can only see a small portion of the different types of light. This light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. This spectrum is made up of all the types of electromagnetic, or EM, radiation in the world and possibly in the universe. EM radiation travels in waves, and each type has a different wavelength.
Visible light, which is the light that people can see, has medium-length waves. Radio waves have the longest wavelengths. Microwaves and infrared light waves also are longer than visible light waves. Ultraviolet (or “UV”) rays, X-rays and gamma rays all have wavelengths that are shorter than visible light. The shorter the wavelength, the more energy the radiation has. Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths; therefore they have the most energy.
Gamma rays have more than 1 billion times the energy of visible light. Gamma rays have so much energy they could harm people on Earth. People are protected from gamma rays by Earth’s atmosphere. The atmosphere absorbs gamma rays, preventing them from affecting life on Earth. Because gamma rays cannot penetrate Earth’s atmosphere, scientists use satellites in space to study them.
Why Is NASA Studying Gamma Rays?
Gamma rays come from the most extreme places in the universe. NASA is studying them because scientists want to learn more about the high-energy environments in the universe that make gamma rays. Gamma rays often come from objects like black holes and exploding stars.
Gamma rays sent out by objects embedded inside galaxies greatly affect the space around these objects and how these galaxies evolve. By studying gamma rays, NASA can better understand how the laws of physics work in the extreme environments found in the distant universe.
How Does Fermi Work?
The Fermi telescope has two main instruments. It has a large telescope that finds gamma rays with 10 million to more than 300 billion times the energy of visible light.
The spacecraft also has detectors that observe gamma-ray bursts. Gamma-ray bursts are brief flashes of gamma rays. Scientists think most of these bursts come from exploding stars that become black holes as their cores collapse.
More than half of the known gamma-ray sources are mysterious. Scientists do not know what causes the gamma rays to be emitted from these sources.
The information from Fermi is sent back to scientists on Earth. The scientists use the data to create pictures of the objects Fermi studies. These pictures help scientists discover the sources of gamma rays.
Comments